Basic Data Structures: Modify an Array Stored in an Object
Now you've seen all the basic operations for JavaScript objects. You can add, modify, and remove key-value pairs, check if keys exist, and iterate over all the keys in an object. As you continue learning JavaScript you will see even more versatile applications of objects. Additionally, the optional Advanced Data Structures lessons later in the curriculum also cover the ES6 Map and Set objects, both of which are similar to ordinary objects but provide some additional features. Now that you've learned the basics of arrays and objects, you're fully prepared to begin tackling more complex problems using JavaScript!
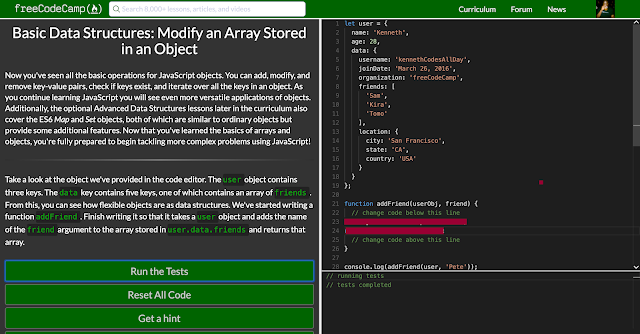
Take a look at the object we've provided in the code editor. The user object contains three keys. The data key contains five keys, one of which contains an array of friends. From this, you can see how flexible objects are as data structures. We've started writing a function addFriend. Finish writing it so that it takes a user object and adds the name of the friend argument to the array stored in user.data.friends and returns that array.
Now you've seen all the basic operations for JavaScript objects. You can add, modify, and remove key-value pairs, check if keys exist, and iterate over all the keys in an object. As you continue learning JavaScript you will see even more versatile applications of objects. Additionally, the optional Advanced Data Structures lessons later in the curriculum also cover the ES6 Map and Set objects, both of which are similar to ordinary objects but provide some additional features. Now that you've learned the basics of arrays and objects, you're fully prepared to begin tackling more complex problems using JavaScript!
Take a look at the object we've provided in the code editor. The user object contains three keys. The data key contains five keys, one of which contains an array of friends. From this, you can see how flexible objects are as data structures. We've started writing a function addFriend. Finish writing it so that it takes a user object and adds the name of the friend argument to the array stored in user.data.friends and returns that array.